Fish Redux中的Dispatch是怎么实现的?
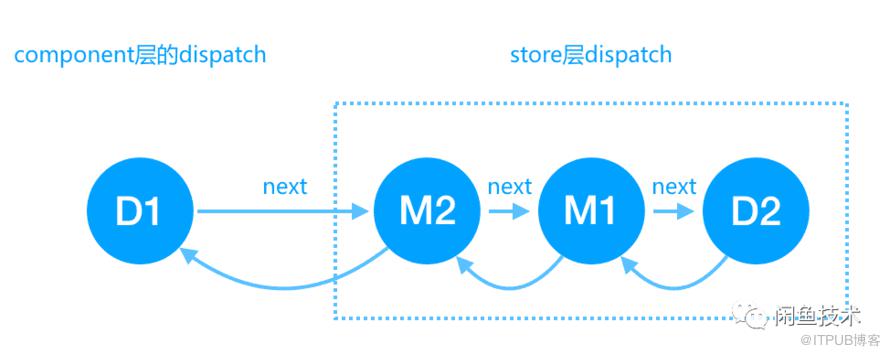
前言 开源地址:https://github.com/alibaba/fish-redux 我们在使用fish-redux构建应用的时候,界面代码(view)和事件的处理逻辑(reducer,effect)是完全解耦的,界面需要处理事件的时候将action分发给对应的事件处理逻辑去进行处理,而这个分发的过程就是下面要讲的dispatch, 通过本篇的内容,你可以更深刻的理解一个action是如何一步步去进行分发的。 为了更好的理解action的dispatch过程,我们就先以todolistpage中一条todo条目的勾选事件为例,来看点击后事件的传递过程,通过断点debug我们很容易就能够发现点击时候发生的一切,具体过程如下: 用户点击勾选框,GestureDetector的onTap会被回调 通过buildView传入的dispatch函数对doneAction进行分发,发现todo_component的云服务器提供商effect中无法处理此doneAction,所以将其交给pageStore的dispatch继续进行分发 pageStore的dispatch会将action交给reducer进行处理,故doneAction对应的_markDone会被执行,对state进行clone,并修改clone后的state的状态,然后将这个全新的state返回 然后pageStore的dispatch会通知所有的listeners,其中负责界面重绘的_viewUpdater发现state发生变化,通知界面进行重绘更新 Dispatch在fish-redux中的定义如下 本质上就是一个action的处理函数,接受一个action,然后对action进行分发。 下面我门通过源码来进行详细的分析。 01 component中的dispatch buildView函数传入的dispatch是对应的component的mainCtx中的dispatch, _mainCtx和componet的关系如下 component->ComponentWidget->ComponentState->_mainCtx->_dispatch而 _mainCtx的云南idc服务商初始化则是通过componet的createContext方法来创建的,顺着方法下去我们看到了dispatch的初始化 // redux_component/context.dart DefaultContext初始化方法 DefaultContext({ @requiredthis.factors, @requiredthis.store, @requiredBuildContext buildContext, @requiredthis.getState, }):assert(factors !=null), assert(store !=null), assert(buildContext !=null), assert(getState !=null), _buildContext = buildContext { finalOnAction onAction = factors.createHandlerOnAction(this); /// create Dispatch _dispatch = factors.createDispatch(onAction,this, store.dispatch); /// Register inter-component broadcast _onBroadcast = factors.createHandlerOnBroadcast(onAction,this, store.dispatch); registerOnDisposed(store.registerReceiver(_onBroadcast)); } context中的dispatch是通过factors来进行创建的,factors其实就是当前component,factors创建dispatch的时候传入了onAction函数,以及context自己和store的dispatch。onAction主要是进行Effect处理。这边还可以看到,进行context初始化的最后,还将自己的onAction包装注册到store的广播中去,这样就可以接收到别人发出的action广播。 Component继承自Logic // redux_component/logic.dart @override Dispatch createDispatch( OnAction onAction,Context<T> ctx,Dispatch parentDispatch){ Dispatch dispatch =(Action action){ throwException( Dispatching while appending your effect & onError to dispatch is not allowed.); }; /// attach to store.dispatch dispatch = _applyOnAction<T>(onAction, ctx)( dispatch:(Action action)=> dispatch(action), getState:()=> ctx.state, )(parentDispatch); return dispatch; } staticMiddleware<T> _applyOnAction<T>(OnAction onAction,Context<T> ctx){ return({ Dispatch dispatch,Get<T> getState}){ return(Dispatchnext){ return(Action action){ finalObject result = onAction?.call(action); if(result !=null&& result !=false){ return; } //skip-lifecycle-actions if(action.type isLifecycle){ return; } if(!shouldBeInterruptedBeforeReducer(action)){ ctx.pageBroadcast(action); } next(action); }; }; }; } } 上面分发的逻辑大概可以通过上图来表示 通过onAction将action交给component对应的effect进行处理 当effect无法处理此action,且此action非lifecycle-actions,且不需中断则广播给当前Page的其余所有effects 最后就是继续将action分发给store的dispatch(parentDispatch传入的其实就是亿华云计算store.dispatch) 02 store中的dispatch 从store的创建代码我们可以看到store的dispatch的具体逻辑 // redux/create_store.dart finalDispatch dispatch =(Action action){ _throwIfNot(action !=null,Expected the action to be non-null value.); _throwIfNot( action.type !=null,Expected the action.type to be non-null value.); _throwIfNot(!isDispatching,Reducers may not dispatch actions.); try{ isDispatching =true; state = reducer(state, action); }finally{ isDispatching =false; } finalList<_VoidCallback> _notifyListeners = listeners.toList( growable:false, ); for(_VoidCallback listener in _notifyListeners){ listener(); } notifyController.add(state); }; store的dispatch过程比较简单,主要就是进行reducer的调用,处理完成后通知监听者。 03 middleware Page继承自Component,增加了middleware机制,fish-redux的redux部分本身其实就对middleware做了支持,可以通过StoreEnhancer的方式将middlewares进行组装,合并到Store的dispatch函数中。 middleware机制可以允许我们通过中间件的方式对redux的state做AOP处理,比如fish-redux自带的logMiddleware,可以对state的变化进行log,分别打印出state变化前和变化后的值。 当Page配置了middleware之后,在创建pageStore的过程中会将配置的middleware传入,传入之后会对store的dispath进行增强加工,将middleware的处理函数串联到dispatch中。 // redux_component/component.dart Widget buildPage(P param){ return wrapper(_PageWidget<T>( component:this, storeBuilder:()=> createPageStore<T>( initState(param), reducer, applyMiddleware<T>(buildMiddleware(middleware)), ), )); } // redux_component/page_store.dart PageStore<T> createPageStore<T>(T preloadedState,Reducer<T> reducer, [StoreEnhancer<T> enhancer])=> _PageStore<T>(createStore(preloadedState, reducer, enhancer)); // redux/create_store.dart Store<T> createStore<T>(T preloadedState,Reducer<T> reducer, [StoreEnhancer<T> enhancer])=> enhancer !=null ? enhancer(_createStore)(preloadedState, reducer) : _createStore(preloadedState, reducer); 所以这里可以看到,当传入enhancer时,createStore的工作被enhancer代理了,会返回一个经过enhancer处理过的store。而PageStore创建的时候传入的是中间件的enhancer。 // redux/apply_middleware.dart StoreEnhancer<T> applyMiddleware<T>(List<Middleware<T>> middleware){ return middleware ==null|| middleware.isEmpty ?null :(StoreCreator<T> creator)=>(T initState,Reducer<T> reducer){ assert(middleware !=null&& middleware.isNotEmpty); finalStore<T> store = creator(initState, reducer); finalDispatch initialValue = store.dispatch; store.dispatch =(Action action){ throwException( Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.); }; store.dispatch = middleware .map((Middleware<T> middleware)=> middleware( dispatch:(Action action)=> store.dispatch(action), getState: store.getState, )) .fold( initialValue, (Dispatch previousValue, DispatchFunction(Dispatch) element)=> element(previousValue), ); return store; }; } 这里的逻辑其实就是将所有的middleware的处理函数都串到store的dispatch,这样当store进行dispatch的时候所有的中间件的处理函数也会被调用。下面为各个处理函数的执行顺序, 首先还是component中的dispatch D1 会被执行,然后传递给store的dispatch,而此时store的dispatch已经经过中间件的增强,所以会执行中间件的处理函数,最终store的原始dispatch函数D2会被执行。 通过上面的内容,现在我们可以知道一个action是如何一步步的派送给effect,reducer去进行处理的,我们也可以通过middleware的方式去跟踪state的变化,这样的扩展性给框架本身带来无限可能。
- 最近发表
- 5、使用企业名称的英文名称作为域名也是国内许多企业选择域名的一种方式,特别适合一些与计算机、网络和通信相关的行业。
- 冷知识!使用 Display: Contents 实现幽灵节点?
- 面试突击:为什么单例一定要加 Volatile?
- 我们是怎么在项目中落地 Qiankun
- 域后缀首选.com,.net,然后是.cn。后缀选择不当,导致流量损失。域名是企业与互联网网址之间的链接,关键是企业在网络上存在的标志。因此,选择好域名是开展网上工作的首要重要条件。
- TienChin 项目中的 RBAC 是怎么玩的?
- 十个用图表解释JavaScript 闭包的面试题
- 从零开始实现一个简单的低代码编辑器
- 域后缀首选.com,.net,然后是.cn。后缀选择不当,导致流量损失。域名是企业与互联网网址之间的链接,关键是企业在网络上存在的标志。因此,选择好域名是开展网上工作的首要重要条件。
- 无差错量子计算机或成现实
- 随机阅读
- 这个不用多说,不同平台的注册价格不同,且不同平台对域名释放交易的把控与曝光不同,当然价格相对便宜且平台渠道广操作便利的平台最好。
- 从 MVC 到 DDD 的架构演进
- 一日一技:如何实现带Timeout的Input?
- 所见即所得的 Markdown 编辑器:Typora
- 最后提醒我们,域名到期后要及时更新域名,否则可能会丢掉域名,每次抢先注册都不会成功。
- 无代码软件发展简史及未来趋势
- 基于重点端到端业务的网元感知画像算法研究
- 系统架构设计之数据模型的选型难题
- 二、如何选择合适的域名
- 应该知道的RPC内核细节(值得收藏)!!!
- 这几个小工具也太好用了!
- 以DevSecOps为主导的七大软件开发趋势
- 小白注册网站域名该怎么办?有什么步骤?
- 一文读懂 TypeScript 泛型及应用
- 前端测试常见的三个误区
- 一次 Eureka 服务下线太慢的惨痛经历!
- 互联网其实拼的也是人脉,域名投资也是一个时效性很强的东西,一个不起眼的消息就会引起整个域名投资市场的动荡,因此拓宽自己的人脉圈,完善自己的信息获取渠道,让自己能够掌握更为多样化的信息,这样才更有助于自己的域名投资。
- 降低前端业务复杂度新视角:状态机范式
- 鲜为人知的CSS实用技巧
- 记录项目日志,一个注解搞定
- 搜索